Debugging
Debugging allows you to monitor internal activity within the system. You can use the debugging tools to:
- Find and fix problems with performance or specific features
- Get detailed information when reporting issues to Kentico support
The following types of debugging are available:
Global system debugs
- Hash tables – provides information about the hash tables used by system objects
- Worker threads – allows you to track and manage background tasks
- Cache items – shows which data is cached in the application’s memory
- Email debugging – allows you to monitor and test the sending of emails from Xperience
Debugs for individual web requests
- SQL queries – shows which SQL queries the system executes when processing requests
- IO operations – allows you to monitor file operations that occur in the system (both input and output)
- Event handlers – displays the system events that were triggered while processing requests
- Macros – allows you to analyze how the system resolves macro expressions
- Cache access – shows the cache operations that the system performs during requests
- Security – shows the details and results of security operations (permission checks)
- Web farm synchronization – monitors the synchronization activity of web farm servers
Enabling debugging
Most debugs are disabled by default, because debugging requires the system to perform extra operations and reduces website performance.
Always disable debugs before deploying websites to the production environment.
To configure debugging, adjust the settings in Settings -> System -> Debug.
The settings in the General category affect debugging globally:
|
Setting |
Description |
|
Disable debugging |
Globally disables all debugging tools, regardless of individual debug settings. |
|
Debug Import/Export |
If disabled, the system does not log debug information for the pages of the Import/Export interface. For performance reasons, it is recommended to leave this option disabled unless you need to debug the Import/Export process. |
|
Debug resources |
If disabled, the debug ignores all resource requests (GetResource and GetCSS). |
|
Debug scheduler |
If disabled, the debug ignores all operations executed by the scheduler. |
Configure individual debug types through the corresponding setting categories. The All category provides equivalent settings that enable all debugs:
|
Setting |
Description |
|
Debug everything everywhere |
Enables:
|
|
Enable all debugs |
Enables all debugs and the corresponding tabs in the interface of the Debug application. |
|
Include UI pages in all debugs |
If checked (true), all enabled debugs include actions performed on the pages of the administration interface. |
|
Default log length |
Sets the default maximum length of the debug log in the Debug application. The default log length is used by debug types that do not have their own log length set. |
|
Display stack information in every debug |
If enabled, the system tracks the code stack for all debug types and displays the information in the Context column of the debug interface in the Debug application. |
|
Log everything to file |
Enables logging of all possible operations into .log files stored in the ~/App_Data/ folder (including the Event log and Email sending log). |
Global system debugs
Global debugs provide general information about the status of the administration application. To access the debug interface, open the Debug application.
System object hash tables
On the System objects tab of the debugging interface, you can view the number of objects stored in the system’s hash tables. The debug shows two types of information:
- The number of records in individual hash tables
- The current number of hashed objects for individual object types
Click Clear hash tables to delete the content of all hash tables.
Worker threads
The system uses worker threads to perform tasks in the background, so that the main application can remain responsive to users. Examples of separate threads in Xperience are Smart search indexing and sending of marketing emails or mass emails.
You can manage threads on the Worker threads tab of the debug interface. Debugging of worker threads can be useful if your application is consuming significantly more resources than expected. Background threads may be the cause.
The debug shows two types of threads:
- Running threads – all worker threads currently running in the system. You can Cancel () individual running threads, or View () their progress log.
- Finished threads – the latest threads that have finished their activity.
Debugs for individual web requests
The system provides debugs for analyzing web requests that occurred during recent activity in the administration interface or on the live site (for certain types of debugs). The recommended way to use web request debugs is to perform actions in one browser tab (or a different browser), and then check the results in the appropriate debug log.
Like with global debugs, you can access the web request debugging interface through the Debug application.
To view the data of all enabled debugs for a specific request, click the request URL in any debug log.
SQL queries
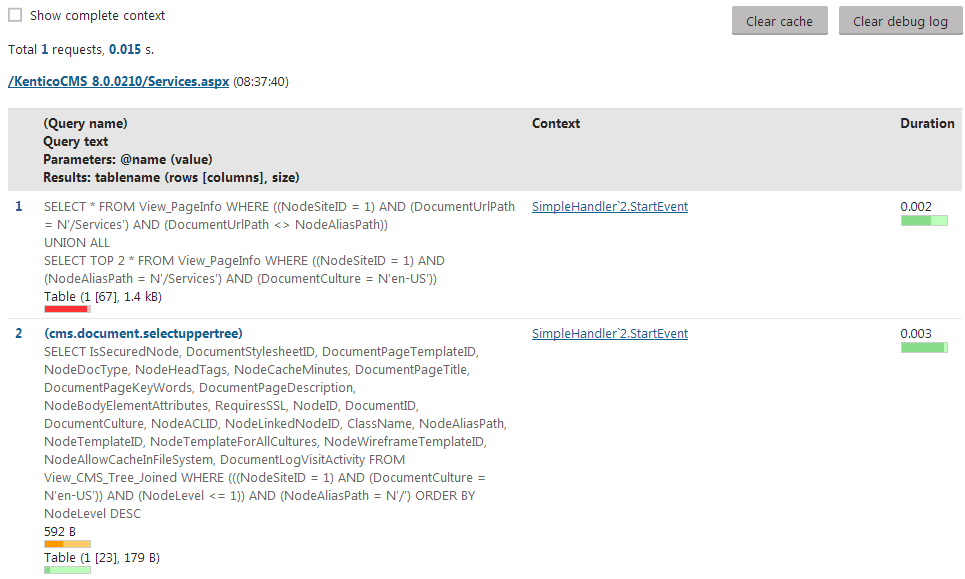
To check which database queries the application executes, select SQL queries in the debugging interface and open either the Live site or Administration tab.
Each tab displays SQL queries executed by the corresponding application, along with queries called within the context of every request. You can find the following information for each query:
- The name and SQL code of the query.
- The Context in which the query was called.
- Click on the method to see the full stack trace.
- If you enable the Show complete context option at the top of the interface, the stack trace is displayed for all queries.
- The Duration of the query execution.
- The total size of the data retrieved by the query.
Click Clear debug log to remove all data in the SQL debug.
The system does not execute SQL queries if the required data is already cached in the application’s memory. If you wish to force pages to execute queries while you are debugging, click Clear cache to flush the application’s cache. Note that you can only clear the cache of the administration application (listed on the Administration tab).
IO operations
The File system (IO) tab of the debugging interface allows you to monitor file operations that occur in the system (both input and output). The IO debug displays a list of recent requests, and all file operations carried out while processing individual requests. For each operation, you can see:
The type of the operation.
The size of the transferred data (if any).
How many times the system accessed the file.
The path of the affected file.
The Context in which the file operation occurred.
- Click on the method to see the full stack trace.
- If you enable Show complete context at the top of the interface, the stack trace is displayed for all operations.
The Provider selector above the debug log allows you to filter the operations for individual file system providers (such as the Local file system, Azure blob storage or Amazon S3). See Configuring file system providers for more information.
Click Clear debug log to remove all data in the IO debug.
Event handlers
On the Event handlers tab of the debugging interface, you can find a list of all events that the system triggered while processing recent requests.
For more information, see:
Click Clear debug log to delete the current data in the event debug (for all requests).