Creating Azure Search indexes
To use Azure Cognitive Search on your website, you first need to prepare indexes that define the scope of the searchable content. For every Azure index in Xperience, the system creates a matching index under a specified Azure Search service. The search functionality then collects the appropriate data from Xperience, uses it to populate the Azure Search indexes, and automatically keeps the indexes up-to-date.
The following types of Azure Search indexes are available:
- Pages – includes the content of pages and products in the site content tree. For more information about page indexing, see the Defining the content of page indexes section.
- General – includes Xperience objects of a specified type.
To learn more about Azure Cognitive Search indexes and their structure, refer to the Creating search indexes in Azure Cognitive Search article.
To create an Azure Search index in Xperience:
Open the Smart search application.
On the Azure indexes tab, click New index.
Configure the general index properties:
Display name – the name of the index displayed in the Xperience administration interface.
Code name – serves as a unique identifier of the index and also sets the index name within your Azure Search service.
Note: Azure Search index names do not allow certain characters that are valid in Xperience code names (for example underscores, see Naming rules for details). When communicating with the Azure Search service, the system automatically omits such characters from the index name.
Index type – determines what type of Xperience content the search index stores.
Batch size – sets the maximum number of records that the system retrieves in a single database query when creating or rebuilding the index. Increasing the value reduces the amount of queries required for large numbers of records, which may improve performance, but also increases memory consumption. The default value is 500. The batch size also limits the number of search documents processed per request to the Azure Search service (this value may additionally be limited by code-level configuration).
Specify your Azure Search service by configuring the Service settings:
Service name – the name of the Azure Search service that will host the index (on Microsoft Azure).
Admin key – the primary or secondary admin key for the Azure Search service. The system uses the key to manage the index, its structure and content. The key grants full rights for all operations within the service.
Query key – optional query key for the Azure Search service. The key can be used by your search interface implementation to search the index while maintaining the principle of least privilege. The query key grants read-only access to all indexes hosted within the service and their content.
To learn how to manage Azure Search services, refer to the Create an Azure Search service in the portal article. For more information about the api keys of search services, see Query your Azure Search.
Click Save.
Configure the content scope of the index. See the corresponding sections:
Return to the General tab and Rebuild the index.
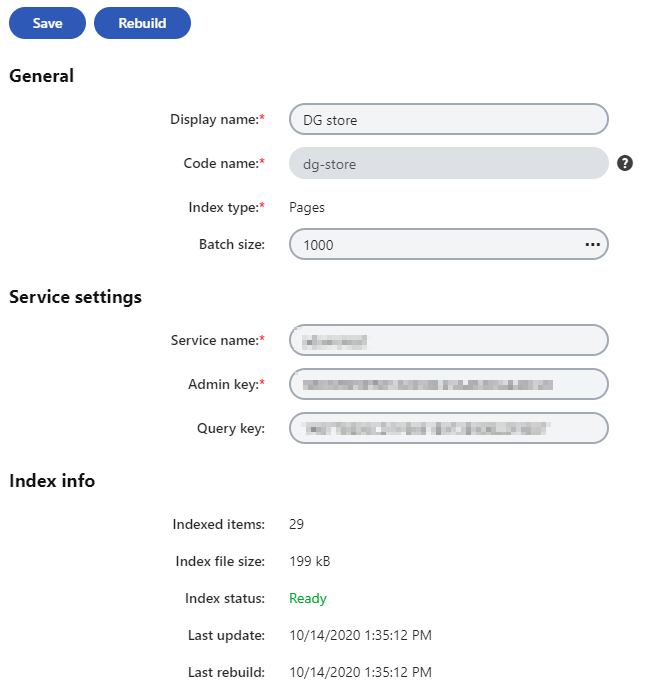
Note: The statistics in the Index info section (indexed items, index file size) do not update immediately after creating or updating an index. There may be a delay of up to several minutes before the statistics are updated in the Azure Search service and displayed correctly in Xperience.
If all configuration is valid and the build succeeds, the index is created and ready for use. You can view the index under the specified Azure Search service in the Microsoft Azure portal.
To allow visitors to search your website using the index, you need to build a custom search interface as described in Integrating Azure Search.
Keeping Azure Search indexes up-to-date
When changes are made to the indexed content, the system automatically updates the search index by logging and processing indexing tasks.
However, if you make changes to the index’s configuration, you need to perform the Rebuild action (deletes the current content of the index and populates it again). The following configuration changes require an index rebuild:
- All options on the General, Sites, Cultures or Indexed content tabs of the index editing interface
- Adjustments of the search field settings for the indexed objects (see the Configuring Azure Search settings for fields section)
- Customizations that adjust how the system builds the index (see Customizing Azure Search)
Note: The Azure Search service only guarantees eventual consistency. When you perform content updates or index rebuilds in Xperience, the changes may not be reflected immediately by the Azure Search. You may experience delays and/or receive outdated results due to the required network communication and the distributed nature of cloud-based services.
Defining the content of page indexes
Pages indexes allow searching through the content of website pages. The indexes only cover pages within the Xperience content tree. Any pages without a representation in the content tree are NOT included (e.g. pages served by custom routes implemented only on the side of the live site application). The indexing mechanism and included content depends on the configuration of individual page types.
The system allows you to configure search indexing separately for each page type. The settings then apply to all search indexes that include pages of the given type.
- Open the Page types application.
- Edit a page type.
- Open the Search tab.
The selectors in the Field mapping for search results section of the interface (Title field, Content field, etc.) do not have any effect for Azure Search indexes. The format of search results is fully controlled by the implementation of your search interface. See Integrating Azure Search.
The Data source for indexing section allows you to select the overall indexing mechanism for the page type. Choose one of the following Data source options:
|
HTML output |
Directly parses the HTML output of pages on the live site, which allows the search to find any text located on pages. Pages are indexed using a web crawler, based on the structure of the content tree in Xperience. Recommendation: Use the HTML output source on sites that use content tree-based routing, for page types whose important content is created using the page builder. Tip: You can perform additional configuration and customization of the HTML output search crawler. |
|
Content fields |
Indexes the structured content of pages in the content tree, which includes the following page data:
Content fields do NOT include the following:
Recommendation: Use the Content fields source for sections of the website where the important content is stored in page fields, such as products or structured articles. |
|
Both |
Combines both HTML output and Content fields. Suitable for page types that store structured content in fields and also have other content in the page output (for example from the page builder or defined directly in the page code). |
The grid in the Fields indexing options section of the tab determines how the smart search indexes the page type’s fields (as defined on the Fields tab). See Configuring Azure Search settings for fields to learn more.
Once you have your page types configured, specify the content for individual Pages indexes:
- Open the Smart search application.
- Create or edit an Azure Search index of the Pages type.
- Open the Sites tab and assign the websites whose content you wish to index.
- Switch to the Cultures tab and select which language versions of the website’s pages are indexed.
- At least one culture must be assigned for the index to be functional.
- Select the Indexed content tab.
- Click Add allowed content or Add excluded content.
- For each item of included or excluded content, specify pages using a combination of the following options:
- Path – path expression identifying the pages that should be indexed.
- Page types – allows you to limit which page types are included in the index.
- (Optional) Configure the following optional settings to add additional indexed content for pages whose page type uses the Content fields or Both data source for search (selected in the Page types application on the Search tab).
Include attachment content – if selected, the index includes the text content of files attached to the specified pages. See Searching attachment files for more information.
Include categories – if selected, the index stores the display names of Categories assigned to the specified pages. This allows users to find pages that belong to categories whose name matches the search expression.
Values added via the special included content options are stored within the sys_content system field of the Azure Search index.
- Click Save to confirm the settings of each included/excluded content item.
- Switch to the index’s General tab and Rebuild the index.
The index now stores the data of the specified pages.
Excluding individual pages from all indexes
You can also exclude specific pages from all search indexing:
- Open the Pages application.
- Select the given page in the content tree.
- In Edit mode, open the Properties -> Generaltab.
- Select the Exclude from search option.
- Click Save.
Configuring the HTML output search crawler
The web crawler that indexes the HTML output of pages reads content under a user account. You can configure the user for every Pages index (on the General tab of the index editing interface):
|
Index property |
Description |
|
User account for crawler |
Sets the user account under which the crawler indexes pages. Only applies for pages whose page type has the HTML output or Both data source selected in the Page types application on the Search tab. Reading pages under a user allows the crawler to:
If empty, the index uses the user account specified in Settings -> System -> Default user ID (or the default administrator user account if the setting is empty). If you wish to assign a user to your search indexes, we recommend creating a dedicated service account with the appropriate permissions (not an account representing an actual live site user or editor). |
Additionally, developers can customize how the crawler processes page output (the process is the same for both Azure indexes and locally stored indexes).
Defining the content of general indexes
When creating or editing an Azure Search index of the General type in the Smart search application, use the following process to specify the content of the index:
- Open the index’s Indexed content tab and set the following properties:
- Object name – selects the type of objects searched by the index.
- (Optional) Where condition – sets a custom WHERE clause for the queries that retrieve data when building the index. Allows you to limit which objects are included in the index.
- Click Save.
- Switch to the Search fields tab to configure which fields are included in the index (see the Configuring Azure Search settings for fields section for details).
- Click Save.
- Open the General tab and Rebuild the index.
The index now stores the data of the specified objects and fields.
Notes:
- The search field configuration is global for objects of a single type. If you have multiple general indexes for one object type (i.e. using the same Object name), changing the search field settings for one index also affects the others.
- Selections made on the Sites tab do not have any effect for Azure Search indexes of the General type. If you wish to configure a general index to search only through objects assigned to a specific site, we recommend using the Where condition property on the Indexed content tab.
Configuring Azure Search settings for fields
Pages and objects in Xperience are often complex data structures with many different fields. The system allows you to adjust how specific fields are indexed for the Azure Search. Not all fields may be relevant for your search scenario and we recommend indexing only necessary fields to keep your indexes as small (and fast) as possible.
To configure the field search settings for indexes of the Pages type:
Fields of specific page types:
- Open the Page types application.
- Edit a page type.
- Select the Search tab.
Common fields shared by all pages and fields of E-commerce SKUs (products):
- Open the Modules application.
- Edit the E-commerce module.
- Open the Classes tab.
- Edit the SKU class.
- Select the Search tab.
- Click Customize.
To configure the field search settings for indexes of the General type, edit a given index in the Smart search application and open the Search fields tab.
In all cases, the interface contains a Fields indexing options section with a grid where you can configure the following options under the Azure and General sections (to learn about the settings for locally stored indexes, see the Creating local search indexes chapter).
|
Azure |
|
|
Content |
If selected, the field’s value is added to the sys_content system field within the search index. The sys_content field:
|
|
Retrievable |
Sets the corresponding Azure Search attribute for the field. See the Create Index article (Index Attributes section) for detailed information about Azure Search field attributes. |
|
Searchable |
|
|
Facetable |
|
|
Filterable |
|
|
Sortable |
|
|
General |
|
|
Index update trigger |
Only available when configuring search field settings that apply to pages (for individual pages types or via the SKU class). Not supported for General indexes. If selected, any modifications of the field’s value cause the system to update the given page in search indexes. We strongly recommend keeping this option enabled for all fields included in your Azure indexes. For page types that use the HTML output (or Both) data source, enable the option if you wish to ensure that the search re-indexes the output of pages when an editor modifies the given field. |
|
Custom search name |
Sets a custom name for the field within search indexes that overrides the default Xperience field name. |
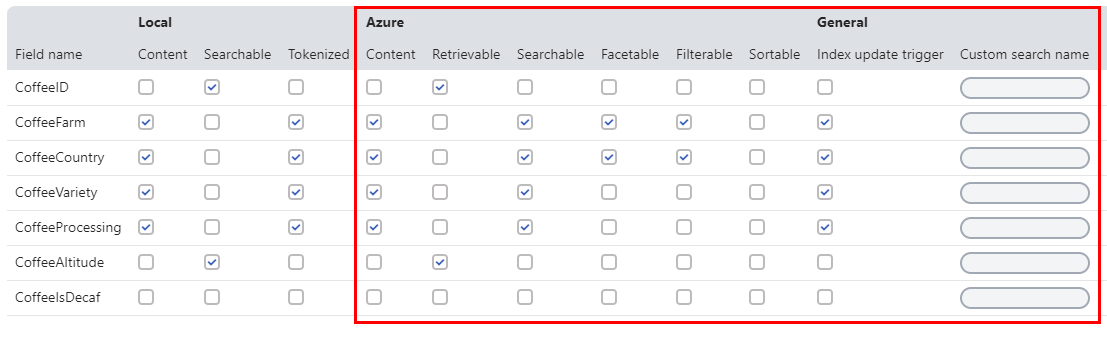
To apply changes, click Save and Rebuild any related Azure Search indexes.
Tip: You can set other field attributes (such as language analyzers) by Customizing the Azure Search.
Note: The selectors in the Field mapping for search results section of the interface (Title field, Content field, etc.) do not have any effect for Azure Search indexes. The format of search results is fully controlled by the implementation of your search interface. See Integrating Azure Search.