Defining website data structure
On this page, you can learn how Kentico stores and organizes data:
Organizing pages and files
All content in Kentico is stored in a tree hierarchy. You can see it in the content tree on the left side the Pages application.
The tree hierarchy provides certain advantages:
- It organizes the page in a logical structure that represents the (dynamic) site map.
- It ensures easy-to-navigate information architecture.
- It provides a logical categorization of pages.
- The content of sub-pages can be nested inside the parent pages.
- The position of the page is reflected in its URL, which consists of the page path in the tree hierarchy,
such as /products/lcd-displays/nec-52vm.aspx. - The structure allows you to define permissions (and other types of settings) for a particular site section and have underlying items inherit them.
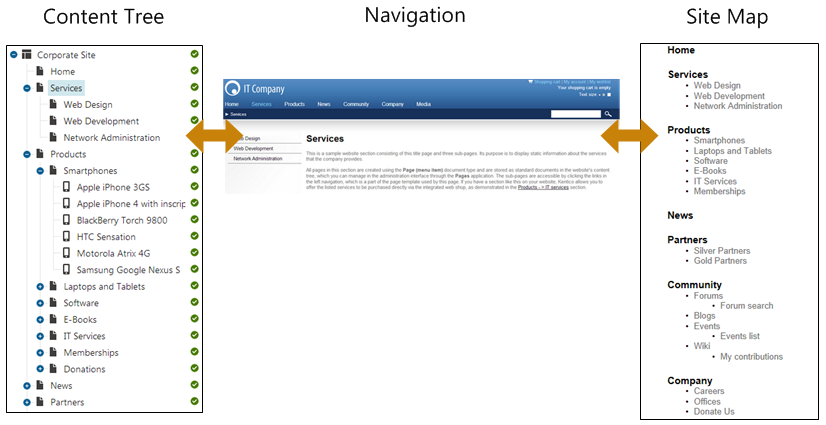
The following figure shows how the content tree defines the navigation and site map of the website:
Page types
Each page is of some type - it can be a page (menu item), a news item, an article, a product specification, etc. Each page type has its own:
- fields (data structure)
- editing form layout
- transformations (appearance and design)
- queries
and other settings.
Page types are fully customizable. You can add, modify and delete custom fields. The advantage of using custom page types is that you can define custom page structure and store content (data) separate from design.
Use the Page types application to manage page types.
Structured pages
While all items in the content tree of the Pages application are pages, there are two types of pages that you can distinguish. There are pages that are set to display content and they are displayed as menu items by default (this can be also customized). Examples of these are the /Home, /Products, /Services on the sample Corporate site. This behavior is enabled by editing individual Page types in the Page types application and enabling the Behave as Page (menu item) option.
The second type of pages are Structured pages, which contain structured data that is then displayed by pages that behave as menu items. Examples of these are the news items under the /News section of the sample Corporate Site.
Pages that are set to behave as menu items usually contain unstructured content in the form of editable regions that can be edited on the Page tab. Structured pages contain structured and typed data stored in page type-specific database tables and edited on the Form tab.
You will typically use structured pages when you need to display a list of items, such as list of news, list of products, etc.
Pages versus Forms
There are two types of content: content stored in editable regions on the page and content stored in forms. The following table compares both approaches:
|
Editable regions on the page |
Form |
|
|
Content structure |
Simple content structure, only text-based content. |
Complex content structures, typed data, such as text, date-time, numbers, etc. |
|
Validation |
Only basic validation rules for minimum and maximum length. |
Complex validation rules, including regular expressions and custom form controls with custom validation code. |
|
Display |
The content is displayed in the context of the page providing truly WYSIWYG editing. |
The content is displayed using XSLT or ASCX transformations using special controls or web parts. |
|
Storage |
The content is stored in a single XML document in the page properties. |
The content is stored in a separate database table. Each field has its own column. The data can be easily modified using SQL queries or API. |
|
Examples of use |
Home page, contact page. Generally: pages with simply structured or unstructured, text-only content. The editable regions are usually used only in connection with pages of type Page (menu item). |
News, product specification, event details, job opening, etc. Generally: pages with structured content where you need to separate content from design and keep the content in its original data type. The form-based content is usually used in connection with pages of type News, Product, Article, etc. |
Organizing media files
There are two types of files you need to manage on the website:
- Website design files - images and flash files that are a part of the website’s design, such as logo, background or menu images. These should be stored in the file system as a part of the application theme.
- Media files and document files - images, flash movies, word documents, PDFs, etc. that are published on the website and are part of the content editable by editors. These should be uploaded to the content tree as pages (the CMS.File page type by default) so that they can be managed by content editors. You can then also apply all content-related features (permissions, workflow, versioning, multilingual support) to these files as well.
You can find more details on files in the Managing files chapter.
Storing data efficiently
The tree hierarchy, in which Kentico stores all content, provides many advantages:
- Organizes pages in a logical structure that represents the (dynamic) site map.
- Ensures an easy-to-navigate information architecture.
- Provides a logical categorization for pages.
- The content of sub-pages can be nested inside parent pages.
- The position of the page is reflected in its URL, which consists of the page path in the tree hierarchy, such as /products/lcd-displays/nec-52vm.aspx.
- The structure allows you to define permissions (and other types of settings) for a particular site section and have underlying items inherit them.
The following figure shows how the content tree defines the navigation and site map of the website:
When storing data in Kentico, you should consider whether you want to store it in Pages, Custom tables or Media libraries. Each of the options was created with different uses in mind and provides various advantages over one another. The following text explains the differences between these approaches.
Pages
Pages offer a hierarchical tree data structure for storing data. You can use them in a workflow or to hold multilingual content without having to use localization macros.
Custom tables
Custom tables provide you with better performance than Pages when storing data in a flat structure. Consider using custom tables when you need to store a large amount of structured items. To localize custom table data, you need to use localization macros.
Media libraries
Media libraries are designed to store large files — not exclusively of media character — such as videos, high-res images or packaged files. You can access media library files without overhead as there is no need to query the database to access them.
Pages vs. custom tables
|
Pages |
Custom tables |
|
|
Can hold traditional data types (int, float, …) |
|
|
|
Can hold binary stream data (files) |
|
|
|
Can hold one-to-many data (radio buttons, drop-down lists) |
|
|
|
Data can be formatted using transformations |
|
|
|
Can be used as an E-commerce product |
|
|
|
Can be displayed by ‘Listings’ web parts |
|
|
|
Can be displayed by ‘Navigation’ web parts |
|
|
|
Workflow |
|
|
|
Versioning |
|
|
|
Multilingual content |
|
* |
|
Hierarchical data structure |
|
|
|
Each record has its own URL |
|
* |
|
Data can be accessed using API |
|
|
|
Importable / Exportable |
|
|
|
Performance |
||
|
Recommended for large data sets when using flat data structure |
|
|
|
Number of database tables that store the data |
3+ |
1 |
|
Recommended for large binary data |
|
|
|
Binary data can be stored in file system |
|
|
*You can translate custom table data using localization macros only.
**You can access custom table records via listing web parts and query string URL parameters.
Pages vs. media libraries
|
Pages |
Media libraries |
|
|
Recommended for large binary data |
|
|
|
Direct access to the data without querying database |
|
|
|
Number of database tables that store the data |
3+ |
2 |
|
Binary data can be stored in file system |
|
|