UI page permission checks
This page covers how to add permissions to applications and evaluate them within UI pages using the role-based access control model.
Add and evaluate permissions for applications
Define the set of application permissions
Each application in the admin UI needs to declare the set of permissions it actively evaluates. This set is reflected when assigning permissions to roles via the Role management application. Define the permissions by decorating UI application pages with the UIPermission attribute and specifying permission names. The system’s default application permissions (VIEW, CREATE, DELETE, UPDATE) are accessible via the SystemPermissions class.
using CMS.Membership;
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base;
// Adds the default application permissions to the 'OfficeManagement' application
[UIPermission(SystemPermissions.VIEW)]
[UIPermission(SystemPermissions.CREATE)]
[UIPermission(SystemPermissions.DELETE)]
[UIPermission(SystemPermissions.UPDATE)]
// Adds a custom permission to the application
// Permission semantics are implementation-dependent
[UIPermission("Acme.HumanResources", "Human resources")]
public class OfficeManagementApplication : ApplicationPage
For applications without any permission requirements, use the NoPermissionRequired attribute. The attribute ensures global visibility and accessibility to all users, regardless of their roles or permissions.
using CMS.Membership;
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base;
// Ensures global visibility and accessibility to all users, regardless of their roles or permissions
[NoPermissionRequired]
public class OfficeManagementApplication : ApplicationPage
Require permissions to access UI pages
To place UI pages behind permissions, use the UIEvaluatePermission attribute. This permission must be from the set defined for the corresponding application using the UIPermission attribute. Otherwise, you would be unable to assign this permission to roles via Role management.
using CMS.Membership;
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base;
// Only roles with the 'Human resources' permission can access this page
[UIEvaluatePermission("Acme.HumanResources")]
public class OpenPositionListing : ListingPage
Permission evaluation in UI page templates
The following UI page templates provided by the API by default contain permission checks:
- Listing pages – require VIEW to access.
- Create pages – require CREATE to access.
Roles without proper permissions attempting to access such pages receive a forbidden (HTTP 403) response.
Evaluate permissions within page commands
You can configure each page command to evaluate a single permission:
// Only roles with the 'CREATE' permission can call this command
[PageCommand(Permission = SystemPermissions.CREATE)]
public async Task<ICommandResponse<RowActionResult>> DoSomething()
{
// Command logic
}
Propagate permission information to client UI templates
You might need to send information about a user’s permissions to the client UI template to, for example, disable certain interactive elements. To check whether the current user has the required permissions, use IUIPermissionEvaluator:
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base;
public class HrPage : Page<PageClientProperties>
{
private readonly IUIPermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator;
public HrPage(IUIPermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator)
{
this.permissionEvaluator = permissionEvaluator;
}
// Sends the required data to the client.
// Based on this information, the logic within the template can, e.g., disable interactive elements
public override async Task<PageClientProperties> ConfigureTemplateProperties(PageClientProperties properties)
{
var permissionResult = await permissionEvaluator.Evaluate("Acme.HumanResources");
properties.HrPermission = permissionResult.Succeeded;
return properties;
}
}
public class PageClientProperties : TemplateClientProperties
{
public bool HrPermission { get; set; }
}
UI permission model and page extenders
If you need to add permissions to system pages or pages provided via third-party integrations where you cannot access the source code, you can do so via UI page extenders:
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base;
// Adds a custom permission to the user listing page in the 'Users' application
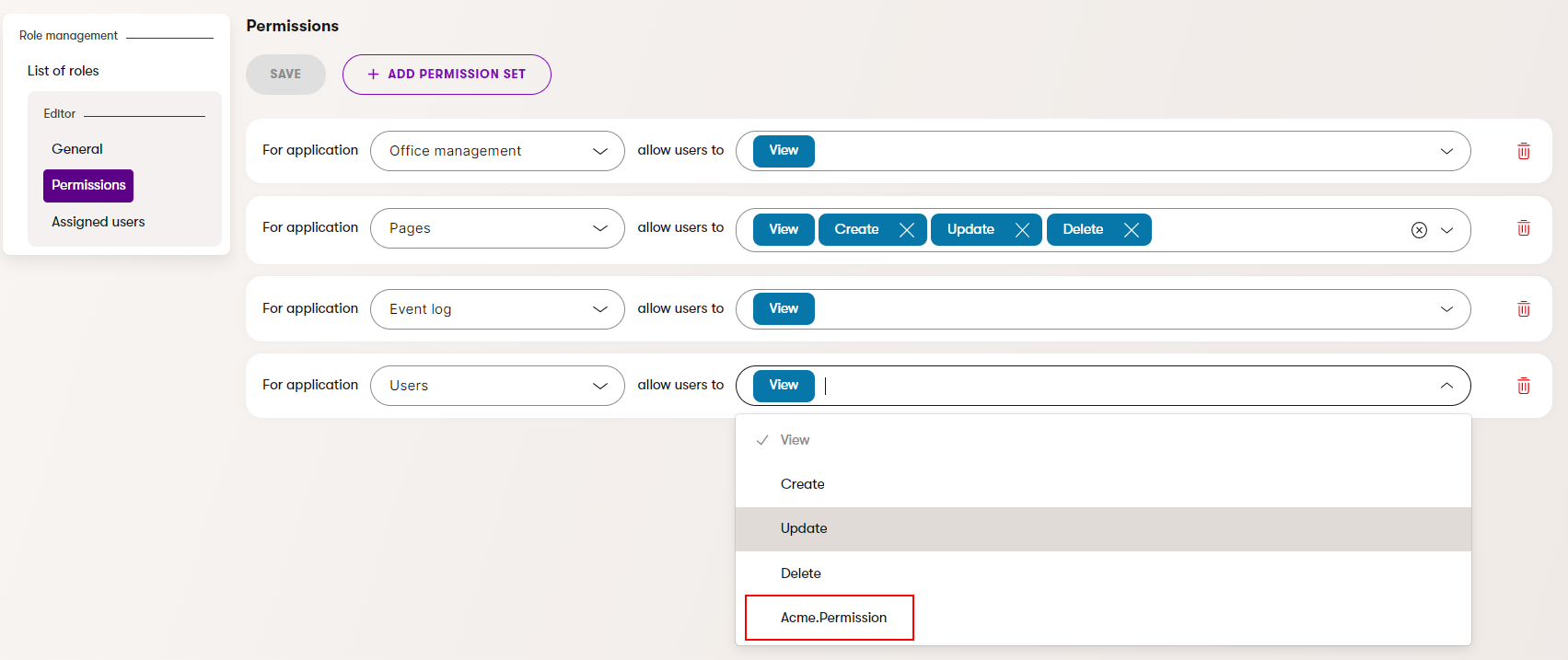
[UIPermission("Acme.Permission")]
public class UserListExtender : PageExtender<UserList>
This applies only to application permissions that you can grant to roles via the Role management application. The page permissions of website channel applications cannot be extended.
After annotating the extender class as demonstrated in the example above, you can work with the added permission as if it was assigned directly to the application. The following example defines a new action on the users listing page from the Users application and places it behind the “Acme.Permission” permission.
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base;
[UIPermission("Acme.Permission")]
public class UserListExtender : PageExtender<UserList>
{
public override Task ConfigurePage()
{
...
configuration.TableActions
.AddCommand("Do something", nameof(DoSomething), Icons.ArrowsCrooked);
...
}
[PageCommand(Permission = "Acme.Permission")]
public async Task<ICommandResponse<RowActionResult>> DoSomething()
{
// Command logic
}
}
The added permission is now also assignable via the Role management application.
Add and evaluate permissions in workspace-scoped applications
Applications scoped under workspaces use the workspace permission model, where permissions can be set for each workspace separately. This model allows you to control access to UI pages and commands in a workspace-scoped application based on workspace-specific permissions.
Require permissions to access workspace-scoped UI pages
To place UI pages behind permissions of a given workspace, use the WorkspaceEvaluatePermission attribute.
using CMS.Membership;
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base;
// Only roles with the 'Create' permission can access this page
[WorkspaceEvaluatePermission(WorkspaceDataPermissions.CREATE)]
public class CustomListing : ListingPage
Evaluate permissions with IWorkspacePermissionEvaluator
Use the IWorkspacePermissionEvaluator to granularly evaluate the permissions for a given workspace specified by the WorkspaceId. You can retrieve the WorkspaceId using the GetContentItemMetadata method or directly from the URL of UI pages that use the WorkspaceId as a parameter of a URL slug.
private readonly IWorkspacePermissionEvaluator workspacePermissionEvaluator;
private readonly IContentItemManagerFactory contentItemManagerFactory;
private readonly IAuthenticatedUserAccessor userAccessor;
private readonly IContentQueryExecutor contentQueryExecutor;
// Mandatory constructor providing instances of required services to the base class
// Can be used to initialize additional dependencies via dependency injection
public CustomPage(IWorkspacePermissionEvaluator workspacePermissionEvaluator,
IContentItemManagerFactory contentItemManagerFactory,
IAuthenticatedUserAccessor userAccessor,
IContentQueryExecutor contentQueryExecutor)
{
}
[PageCommand]
public async Task<ICommandResponse> CommandHandler()
{
// Gets the id of the item from which to retrieve the WorkspaceId
string STORE_CONTENT_TYPE = "Wonka.CandyStore";
ContentItemQueryBuilder builder =
new ContentItemQueryBuilder()
.ForContentType(STORE_CONTENT_TYPE, q =>
{
q.TopN(1)
.Where(w => w.WhereEquals("StoreName", "Prague-Hradcany"));
});
var itemId = await contentQueryExecutor
.GetResult<int>(builder, rowData =>
{
var contentItemId = rowData.ContentItemID;
return contentItemId;
});
var id = itemId.FirstOrDefault();
// Gets the current user in the administration
var user = await userAccessor.Get();
// Creates an instance of the manager class facilitating content item operations
var manager = contentItemManagerFactory.Create(user.UserID);
// Retrieves ContentItemMetadata of a given content item
var metadata = await manager.GetContentItemMetadata(id, CancellationToken.None);
// Evaluates a given permission for the current user and the workspace specified by the WorkspaceId acquired from ContentItemMetadata
// The Succeeded boolean property of IWorkspacePermissionEvaluator indicates the result of the evaluation
if ((await workspacePermissionEvaluator.Evaluate(WorkspaceDataPermissions.VIEW, typeof(ContentHubApplication), metadata.WorkspaceId)).Succeeded)
{
// ...
}
// ...
return Response();
}