Manage page URLs
Xperience allows you to modify URLs of web pages on the URLs tab when editing a page in a website channel application. The system can also track changes of URLs and store old URLs for redirection purposes. These former URLs can be managed in the URLs application.
The following types of URLs are available for pages:
- System URL – Default URL generated from the page’s position in the content tree using the page’s URL slug and URL slugs of the page’s ancestors. The ‘slug’ is the part that comes at the very end of a URL, and refers to a specific page or post. For example, for the URL example.com/Articles/News/Tea-Blends/, the URL slug is ’Tea-Blends’. For more information about how page URLs are generated, see Page URL generation.
- Vanity URL – Alternative URL that can be configured and customized by marketers. One page can have multiple vanity URLs. All configured vanity URLs across all pages are displayed in the URLs application. Vanity URLs can serve multiple purposes:
- Marketing and branding – You can create URLs that promote branding of your products and include recognizable words to improve your marketing reach.
- Sharing – You can create a URL that is short and can be copied and shared easily, for example, on social media.
- SEO – You can improve the SEO of the page by including SEO keywords in the URL of the page.
- Canonical URL – Preferred URL of a page, i.e., the URL that is displayed to the user in the browser URL bar and is intended to be indexed by search engines. All URLs representing a page redirect to the canonical URL of the page via a “301 Moved Permanently” redirect. By default, the system URL is the canonical URL for each page. You can decide to set a vanity URL as the canonical URL of a page.
You can also create a temporary shareable preview URL and send it to reviewers who can’t access the administration. This URL is not intended for regular live site visitors.
Edit URL slugs of pages
You may not be able to edit URL settings of every page. This depends on the configuration of the page’s underlying content type. If you are not sure, consult with your site’s administrator.
When you create a new page, the slug is automatically generated from the page’s title. Past this point, any changes to the page title do not get reflected in the slug. You need to change it manually if required:
Open a website channel application.
In the content tree, select the page you want to edit.
Make sure the page is in the Draft status or another custom workflow step.
- When a page is Published or Unpublished, you need to select Edit page or Create new version in the Content view mode. This transitions the page to the Draft step and enables editing and publishing of the page.
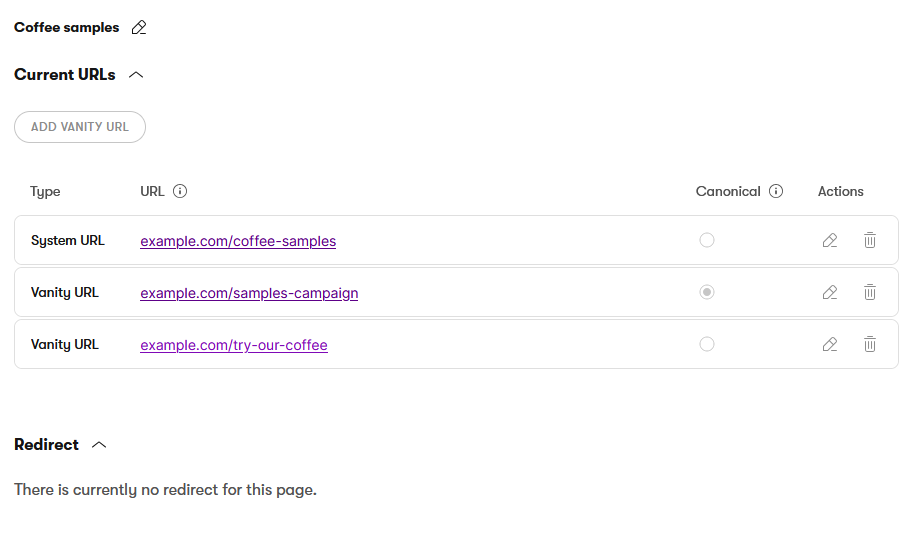
On the URLs tab, edit () the System URL.
Edit the URL slug in the dialog window and Save it.
- Note: Changing URL slug of a page may also affect URLs of all of the page’s descendants.
- Some characters may be forbidden from use in URLs (e.g., ‘#’, ‘/’, ‘$’, ‘&’), depending on the settings of your site. Administrators can adjust these settings in Settings → URLs and SEO → URL format.
Save the change.

You have now successfully changed the URL slug of the page. Note that the page is now a Draft. The page needs to be published in order to be accessible under the new system URL.
Manage vanity URLs of pages
You may not be able to edit URL settings of every page. This depends on the configuration of the page’s underlying content type. If you are not sure, consult with your site’s administrator.
Vanity URLs are optional for pages and can be set at any time after a page is created. Once created, a vanity URL can be set as the canonical URL of the page. A page can have multiple vanity URLs. You can see all vanity URLs used across the system in the URLs application.
Add vanity URLs to pages
Open a website channel application.
In the content tree, select the page you want to edit.
Make sure the page is in the Draft status or another custom workflow step.
- When a page is Published or Unpublished, you need to select Edit page or Create new version in the Content view mode. This transitions the page to the Draft step and enables editing and publishing of the page.
Select Add vanity URL in the Current URLs section.
Enter the Vanity URL path and confirm with Add.
- Some characters may be forbidden from use in URLs (e.g., ‘#’, ‘/’, ‘$’, ‘&’), depending on the settings of your site. Administrators can adjust these settings in Settings → URLs and SEO → URL format.
Save the change.

You have now successfully added the new vanity URL of the page. Note that the page is now a Draft. The page needs to be published in order to be accessible under the new URL.
Edit vanity URLs of pages
To edit a vanity URL of a page:
Navigate to the page whose vanity URL you want to edit. You can do so by:
- Opening the corresponding website channel application and selecting the page in the content tree.
- Going to the Vanity URLs tab in the URLs application and opening () the page corresponding to the chosen vanity URL.
Make sure the page is in the Draft status or another custom workflow step.
- When a page is Published or Unpublished, you need to select Edit page or Create new version in the Content view mode. This transitions the page to the Draft step and enables editing and publishing of the page.
On the URLs tab, edit () the Vanity URL you want to change.
Edit the Vanity URL path in the dialog window and Save it.
- Some characters may be forbidden from use in URLs (e.g., ‘#’, ‘/’, ‘$’, ‘&’), depending on the settings of your site. Administrators can adjust these settings in Settings → URLs and SEO → URL format.
Save the change.

You have now successfully changed the vanity URL of the page. Note that the page is now a Draft. The page needs to be published in order to be accessible under the new URL.
Delete vanity URLs of pages
Open a website channel application.
In the content tree, select the page that you want to edit.
Make sure the page is in the Draft status or another custom workflow step.
- When a page is Published or Unpublished, you need to select Edit page or Create new version in the Content view mode. This transitions the page to the Draft step and enables editing and publishing of the page.
On the URLs tab, delete () the desired Vanity URL and confirm the deletion.
Save the change.

You have now successfully deleted the vanity URL of the page. Note that the page is now a Draft. The page needs to be published to make it inaccessible under the deleted vanity URL.
Select the canonical URL of pages
You may not be able to edit URL settings of every page. This depends on the configuration of the page’s underlying content type. If you are not sure, consult with your site’s administrator.
Canonical URL is the preferred URL of a page, i.e., the URL that is displayed to the user in the browser URL bar and is intended to be indexed by search engines.
- All URLs representing a page redirect to the canonical URL of the page via a “301 Moved Permanently” redirect.
- All system features (e.g., URL selector, rich text editor, page URL retriever, email template macros) use and return the canonical URLs of pages.
- By default, the system URL is the canonical URL for each page.
To set a URL as the canonical URL:
Open a website channel application.
In the content tree, select the page that you want to edit.
Make sure the page is in the Draft status or another custom workflow step.
- When a page is Published or Unpublished, you need to select Edit page or Create new version in the Content view mode. This transitions the page to the Draft step and enables editing and publishing of the page.
On the URLs tab, select the Canonical option for the URL you want to make canonical. You can select from the page’s vanity URLs and its system URL.
Save the change.

The selected URL is now configured as the canonical URL of the page. Note that the page is now a Draft. The page needs to be published to apply the change.
Canonical URL of the home page
The canonical URL of the home page of your website channel is, regardless of what URL is selected as canonical by the user, always the root URL of your website (i.e., https://example.com/) for the primary language and https://example.com/<language_name>/ for other languages.
Manage redirects from unpublished pages
You can edit active and scheduled redirects from unpublished pages on the URLs tab of the corresponding page. Active redirects can also be edited in the URLs application on the Former URLs tab. The advantage of the URLs application is that you can see and edit all redirects in one place. If no redirect was created when the page was unpublished, you can add it only on the URLs tab of the corresponding unpublished page.
Add redirects from unpublished pages
To add a redirect from an unpublished page with no redirect:
- Open a website channel application.
- In the content tree, select the unpublished page you want to edit.
- On the URLs tab, select Add redirect in the Redirect section.
- In the sidebar, use Select existing page to choose the target page of the redirect.
- Confirm the target with the Select button.
- Save the redirect.
You have now successfully added the redirect. When visitors try to reach the unpublished page, they are redirected to the page you selected.
Edit redirects from unpublished pages
To edit an existing redirect on the URLs tab:
- Open a website channel application.
- In the content tree, select the unpublished page you want to edit.
- On the URLs tab, select Edit in the Redirect section.
- In the sidebar, use Select existing page to change the target of the redirect to another page.
- Confirm the target with the Select button.
- Save the changes.
Alternatively, you can edit existing redirects in the URLs application:
- Open the URLs application.
- Go to the Former URLs tab.
- Select the former URL representing the redirect you want to edit.
- Use Select existing page to select the new target of the redirect.
- Confirm the target with the Select button.
- Save the changes.
You have now successfully edited the redirect. When visitors try to reach the unpublished page, they are redirected to the page you selected.
Delete redirects from unpublished pages
If you want to delete a redirect from an unpublished page, you need to publish the page and unpublish it again without selecting a page to redirect to.
Manage redirects from deleted pages
As deleted pages are no longer available in the system, redirects from deleted pages can be edited and deleted only in the URLs application. If no redirect was created when the page was deleted, a redirect from such a page can be added only via code.
Edit redirects from deleted pages
To edit a redirect from a deleted page:
- Open the URLs application.
- Go to the Former URLs tab.
- Select the former URL you want to edit.
- Use Select existing page to select the new target of the redirect.
- Confirm the changes with the Select button.
- Save the changes.
You have now successfully edited the redirect. When visitors try to reach the unpublished page, they are redirected to the page you selected.
Delete redirects from deleted pages
Once a redirect from a deleted page has been deleted, it cannot be added again in the UI. Such redirects can be added only via code, for example, by developers.
To remove a redirect from a deleted page:
- Open the URLs application.
- Go to the Former URLs tab.
- Remove () the former URL representing the redirect you want to delete.
The redirect is now permanently removed.
URL collision prevention
A site cannot have two pages with identical URLs. Depending on the situation, the system handles collisions in two ways:
- By appending the page’s GUID at the end of the URL slug of the page. For example: https://example.com/Articles/Tea-Blends-ae64db90387143b1a4562e06b67d1970. This occurs when:
- You move a page and the destination already contains a page with a matching URL slug.
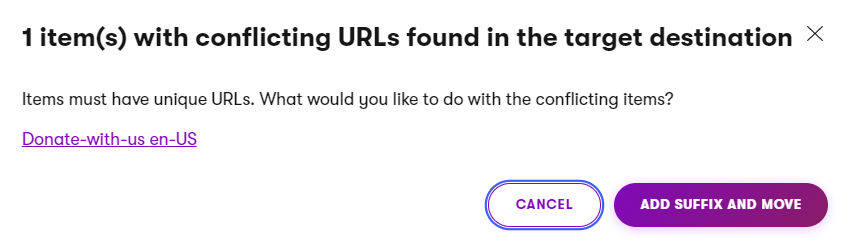
- You move a page and the destination already contains a page with a matching URL slug.
- By preventing the URL from changing and displaying an error message. This occurs when:
- You attempt to change the URL slug or a vanity URL of a page and the resulting URL matches one already in the system.
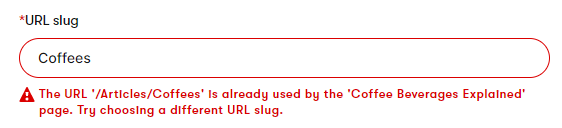
- You attempt to change the URL slug or a vanity URL of a page and the resulting URL matches one already in the system.
Former URLs
The system can automatically keep track of page URL changes by storing old URLs and handling redirects to the current URLs. You can see and manage these redirects in the URLs application on the Former URLs tab. Redirects created by unpublishing or deleting pages are stored and handled by default. You can additionally configure the system to create former URLs when a URL is edited and to redirect to the current URLs.
When a redirect target of a former URL is changed, all redirects that target the corresponding page are also automatically adjusted.
Automatically store edited URLs as former URLs
To configure the system to automatically store edited URLs as former URLs:
- Open the Channel management application.
- Select the website channel for which you want to configure Former URLs to store and handle edited URLs.
- Open Channel settings.
- Select the Store edited URLs as former URLs setting.
- Save the changes.
Former URLs are now created when URLs are edited in the given website channel. Every time a former URL is requested, the system returns a “301 Moved Permanently” response and redirects to the new URL of the page.
If the setting is disabled later, former URLs created up to that point will continue redirecting visitors to current URLs unless the former URLs are removed.
To access a list of all stored old URLs for the website, together with the current URL paths to which they are redirected, open the Former URLs tab in the URLs application.
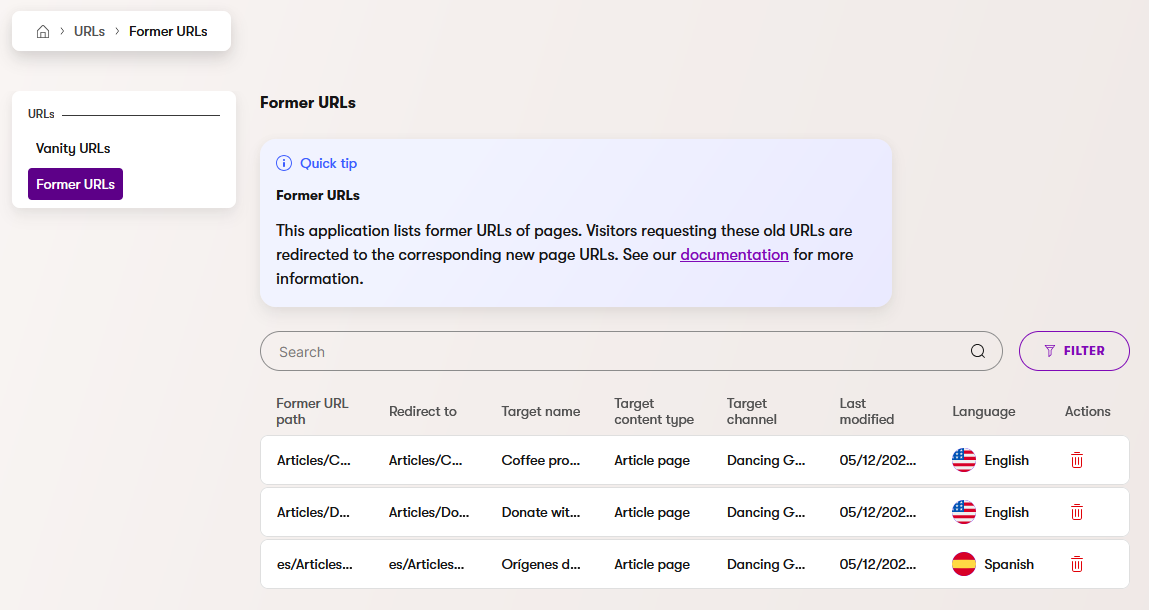
Former URLs scenarios
Former URLs are created when you unpublish or delete a page and also create a redirect from the page. Additionally, you can configure the system to create former URLs when modifying page URLs.
|
Former URLs are always created when: |
If configured to store edited URLs, former URLs are created when: |
|
|
Former URLs are NOT created when:
- Deleting a page without creating a redirect.
- Deleting a page without creating a redirect permanently destroys and removes all former URLs pointing to that page.
- Unpublishing a page and choosing to serve content in the fallback language.
- Unpublishing a page without creating a redirect.
- Administrators perform certain global changes, for example changing the domain of a website channel.
- Changing a language code name.
- Changing the Primary language setting for a website channel.
Changing the language code name or the primary language setting breaks all former URLs for the corresponding language variants of pages.
Remove former URLs created by editing URLs
This action is available only for former URLs created by editing a page’s URL or by deleting a page. Their remove button is active (). Former URLs that are created by unpublishing pages have a disabled delete button () and can’t be deleted.
To remove a former URL:
- Open the URLs application.
- Go to the Former URLs tab.
- Remove () the specific former URL.
The former URL is now permanently removed.