Logging
Xperience by Kentico provides logging functionality that helps monitor application behavior and diagnose issues. The logging implementation is based on .NET logging.
Data is logged from all Xperience modules and features, and developers can use logging within any custom code or components. You can access or visualize the resulting logs in various ways:
- The built-in Xperience event log
- Command line output when running Xperience as a web application
- Any external tool or framework compatible with .NET logging (Serilog, NLog, Aspire dashboard, etc.)
Xperience event log
Xperience provides a built-in XperienceEventLog logging provider, which captures system events and errors. The logged data can be viewed directly within the Xperience administration in the Event log application. This allows developers and administrators to quickly identify and resolve application issues without requiring external tools or third-party services.
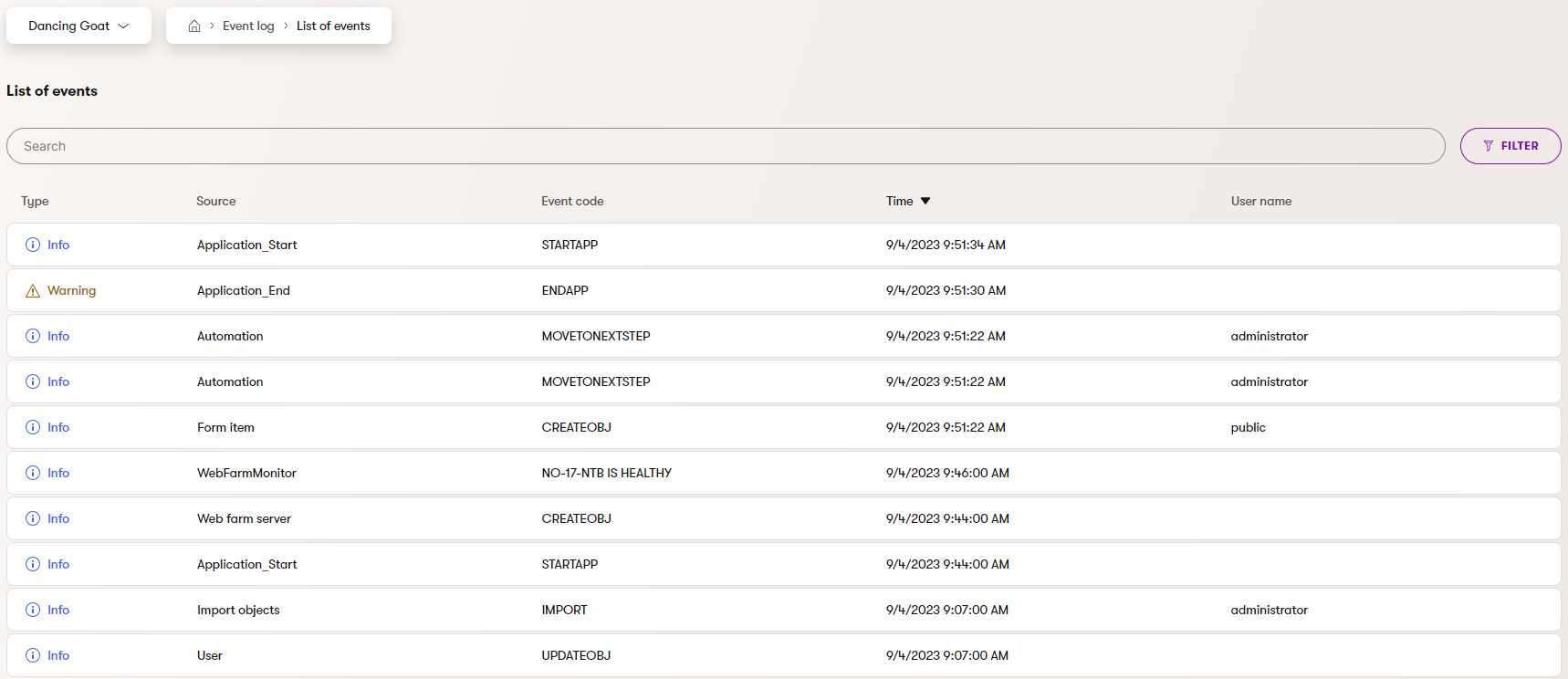
Logged events are stored in the Xperience database. In case of a database outage, the system buffers all logged events in-memory until the database is available. When logging in custom code, you do not need to buffer or check for database availability.
Configure logging
Logging can be adjusted via standard .NET logging configuration in your Xperience project’s appsettings.json file. This allows you to increase or decrease the verbosity of logged data, filter specific events, etc. See Log level to learn more about the available severity and verbosity levels of logged data.
The Xperience event log is represented by the XperienceEventLog logging provider. By default, this provider captures the following logs:
- Events with a log level of
Warningor higher originating from any application code (including custom). - Events with a log level of
Informationor higher originating from the Xperience libraries (CMSandKenticologging categories).
Events with the Information or lower level originating from custom code are not included unless you add configuration for your event categories. See Logging in custom code.
Adjust the configuration if you wish to change or filter which logs appear in the system’s event log (or your own logging providers). You can target events logged from specific Xperience libraries and features by adding configuration for the corresponding namespace.
For example, the configuration shown below for the XperienceEventLog provider does the following:
- Increases logging verbosity to include the
Debuglevel for events originating from loggers in theCMS.ContentSynchronizationnamespace. - Includes events with a
Debugor higher level that are logged with a category starting withAcme(i.e., the output of loggers used in classes from a customAcme.*namespace).
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
},
"XperienceEventLog": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning",
"Kentico": "Information",
"CMS": "Information",
"CMS.ContentSynchronization": "Debug",
"Acme" : "Debug",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.Kestrel": "None"
}
}
},
Logging in custom code
To perform logging in your custom modules, components or other code:
- Obtain an instance of
ILogger<TCategoryName>using dependency injection.- The
TCategoryNamegeneric sets the category for all events created via this logger. The fully qualified name of the specified type is used. The category also determines the Source value for events in the Xperience event log.
- The
- Call one of the available
Log*methods to log an event with a corresponding log level.- To set the Event code value for events in the Xperience event log, include the
EventIdparameter in the call and set itsname.
- To set the Event code value for events in the Xperience event log, include the
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using CMS.Core;
namespace Acme;
public class CustomComponent {
private readonly ILogger<CustomComponent> logger;
// Gets an ILogger instance using constructor DI
// In this example, the logging category is "Acme.CustomComponent"
public CustomComponent(ILogger<CustomComponent> logger)
{
this.logger = logger;
}
// ...
// The Trace, Debug and Information log levels appear as the 'Info' event type in the Xperience event log
// By default, events with these log levels are not written to the Xperience event log
// Can be included by setting the corresponding log level for your event categories in the 'XperienceEventLog' logging provider (appsettings.json)
logger.LogTrace("Trace level event description.");
logger.LogDebug("Debug level event description.");
logger.LogInformation("Information level event description.");
// The Warning log level appears as the 'Warning' event type
logger.LogWarning("Warning event description.");
// The Error and Critical log levels appear as the 'Error' event type
logger.LogError("Error event description.");
logger.LogCritical("Critical event description");
// Logs an event with a specific event code via the 'name' value of an EventId object
// If the EventId parameter is omitted, the event Source is used as the event code
// The 'id' value of the EventId object is not used by the Xperience event log, but may affect other logging providers
logger.LogInformation(new EventId(0, "APIEXAMPLE INFO"), "Information event description.");
// Logs an event (error) with exception details
logger.LogError(new EventId(0, "APIEXAMPLE EXCEPTION"), new Exception(), "Exception event description.");
}
Logged events appear in the Xperience event log (depending on your logging configuration and the used log level) and any other logging providers configured for your application.
You can use the LogWithIntervalPolicy method to ensure that events are logged only once during the application’s lifetime or a specified time interval. This can be useful to limit the frequency of events that could otherwise flood your log.
// Logging policy that ensures the event is logged only once during the application's lifetime
// The system checks whether the event has already been logged based on the identifier of the 'OnlyOnce' method
logger.LogWithIntervalPolicy(LoggingIntervalPolicy.OnlyOnce("api-example-once-per-lifetime"),
log => log.LogInformation("Event logged only once."));
// Logging policy that ensures the event is logged at most once over a specified time interval (5 minutes in this case)
// The system checks whether the event has already been logged based on the identifier of the 'OncePerPeriod' method
logger.LogWithIntervalPolicy(LoggingIntervalPolicy.OncePerPeriod("api-example-once-per-5-minutes", TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5)),
log => log.LogInformation("Event logged at most once every 5 minutes."));
Customize event logging
You can customize event logging by:
- Handling system events – customize event information, limit which types of events the system logs, or execute any custom logic when an event gets written to the Xperience event log.
- Adding custom logging providers – specify additional logging destinations, e.g., dedicated files, third-party logging tools or frameworks, visualization tools, etc.
- Adding or removing the Xperience event logging provider – in advanced scenarios, you may wish to manually control whether the default Xperience event logging provider is enabled for the application.
Handle event log events
You can use event handling to customize how the system writes records into its event log.
The system raises the following types of logging events:
EventLogEvents.LogEvent.Before– allows you to customize the data logged for events or cancel logging for certain types of events.EventLogEvents.LogEvent.After– allows you to perform custom actions after events are successfully logged.
Handlers only affect the built-in event log
Event handlers for EventLogEvents.LogEventonly affect how events are written to the built-in Xperience event log, not log entries created via ILogger in general (e.g., when viewing events in external tools).
Performance considerations
Performing demanding operations during event logging can negatively impact the project’s performance (particularly on websites under heavy load where a large volume of logging can occur).
Example
The following example demonstrates how to disable logging for events of a specific type and modify the Description text for certain events.
- Open your Xperience solution in a suitable IDE (e.g., Visual Studio).
- Create a custom module class.
- Override the module’s
OnInitmethod and assign a handler method toEventLogEvents.LogEvent.Before. - Perform the required actions within the handler method.
- Access the data of the logged event through the
Eventproperty of the handler’sLogEventArgsparameter. - To cancel the logging of an event, call the
Cancelmethod of the handler’sLogEventArgsparameter.
- Access the data of the logged event through the
using CMS;
using CMS.DataEngine;
using CMS.EventLog;
using CMS.Base;
// Registers the custom module into the system
[assembly: RegisterModule(typeof(EventLogCustomization))]
public class EventLogCustomization : Module
{
// Module class constructor, the system registers the module under the name "EventLogCustomization"
public EventLogCustomization()
: base("EventLogCustomization")
{
}
// Contains initialization code that is executed when the application starts
protected override void OnInit()
{
base.OnInit();
// Assigns a handler to the LogEvent.Before event
EventLogEvents.LogEvent.Before += LogEvent_Before;
}
private void LogEvent_Before(object sender, LogEventArgs e)
{
// Gets an object representing the event that is being logged
EventLogInfo eventLogRecord = e.Event;
// Cancels logging for events with the "CREATEOBJ" or "UPDATEOBJ" event codes.
// Disables event log records notifying about the creation or update of objects in the system,
// but still allows events related to object deletion.
string eventCode = eventLogRecord.EventCode;
if (String.Equals(eventCode, "CREATEOBJ", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) || String.Equals(eventCode, "UPDATEOBJ", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
e.Cancel();
}
// Adds a custom message to the Description field for events of the Information type
if (String.Equals(eventLogRecord.EventType, EventType.INFORMATION, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
eventLogRecord.EventDescription += " Custom message";
}
}
}
Custom logging providers
The .NET logging framework allows you to add other logging providers in addition to the Xperience event log. Logging providers store and display logged data, and may provide additional features, such as sematic (structured) logging or advanced visualization.
For more information, see the .NET documentation:
Example
The following example demonstrates how to set up Aspire dashboard to receive log data from Xperience. Aspire dashboard allows you to monitor and debug your applications in a central location, including telemetry data from sources outside of Xperience.
Start by setting up an Aspire AppHost:
- Open your Xperience solution in Visual Studio (or another suitable IDE).
- Add a new project to the solution with the Aspire AppHost project template.
- Add a project reference from the Aspire project to your Xperience project.
- Adjust the Aspire project’s AppHost.cs file:
C#AppHost.cs
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Adds your Xperience project to the Aspire AppHost // Replace the project type and name with values matching your Xperience project var xperienceProject = builder.AddProject<Projects.ProjectName>("XperienceProject"); builder.Build().Run();
Aspire dashboard receives log data using OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP). Continue by adding an OpenTelemetry logger and OTLP exporter to your Xperience project:
- Install the following NuGet packages into your Xperience project:
- Call the
AddLoggingextension method with theAddOtlpExporteroption on the project’s service collection:C#Program.csusing Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using OpenTelemetry.Logs; // ... var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // ... builder.Services.AddLogging(logging => { logging.AddOpenTelemetry(options => { options.IncludeFormattedMessage = true; options.IncludeScopes = true; options.ParseStateValues = true; options.AddOtlpExporter(); }); });
When you run the Aspire application (e.g., dotnet run from the folder where you added the project), the Aspire dashboard launches in a browser. This also automatically starts your Xperience application. You can view logs from Xperience (and any other applications added to the Aspire AppHost) on the dashboard.
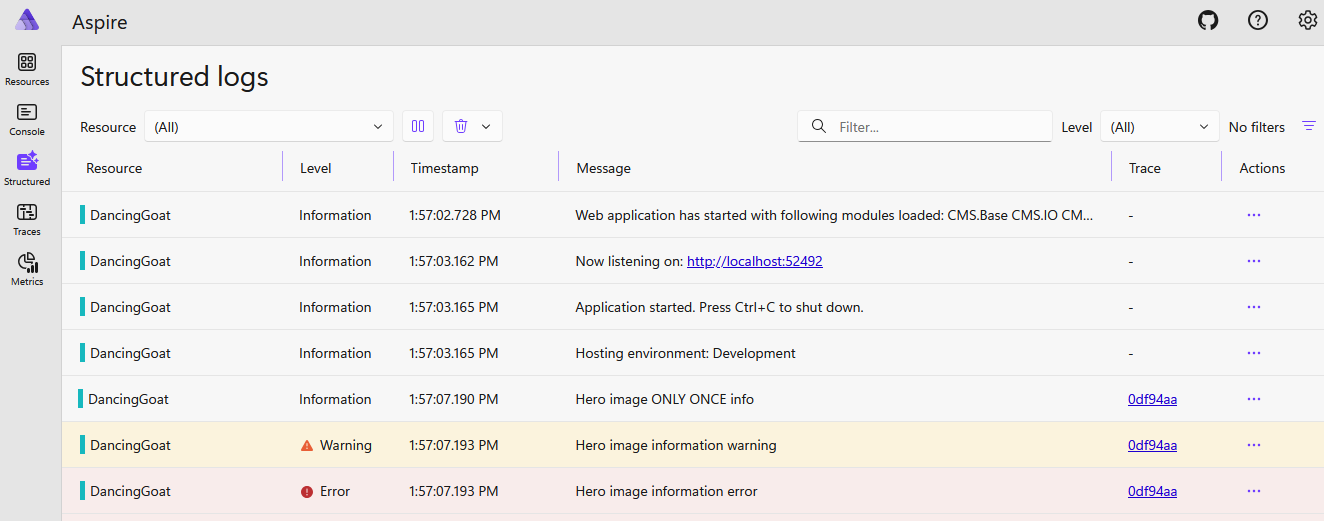
Aspire dashboard standalone mode
You can also run Aspire dashboard as a Docker image in Standalone mode.
Add or remove the Xperience event logging provider
The logging provider for the Xperience event log is enabled by default as part of the InitKentico call in the project’s middleware pipeline.
If you are developing a fully custom logging implementation for your project, you can remove the Xperience event logging provider by calling the ClearProviders extension method before you add your own logging providers.
Application Insights for SaaS projects
Disabling the Xperience event logging provider also affects the Microsoft Application Insights integration for SaaS projects. The Event log report in the Xperience Portal Monitoring application will stop receiving data.
If your implementation clears logging providers, but you also wish to enable the Xperience event logging provider, call the AddXperienceLogging method for your application’s service collection.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using CMS.EventLog;
WebApplicationBuilder builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// ...
services.AddLogging(builder => {
// Removes all logging providers
builder.ClearProviders();
// Add your custom providers
});
// Manually adds the Xperience event logging provider
builder.Services.AddXperienceLogging();
Filtering Xperience events from your logging providers
If you do not wish to include events logged from the Xperience libraries in your logging providers, adjust your project’s logging configuration to filter out events with the CMS or Kentico category prefixes.