Module: Data protection
4 of 13 Pages
Create a cookie consent widget
Let’s dive into the process of creating a cookie configuration page similar to the cookie policy page on Kentico.com.
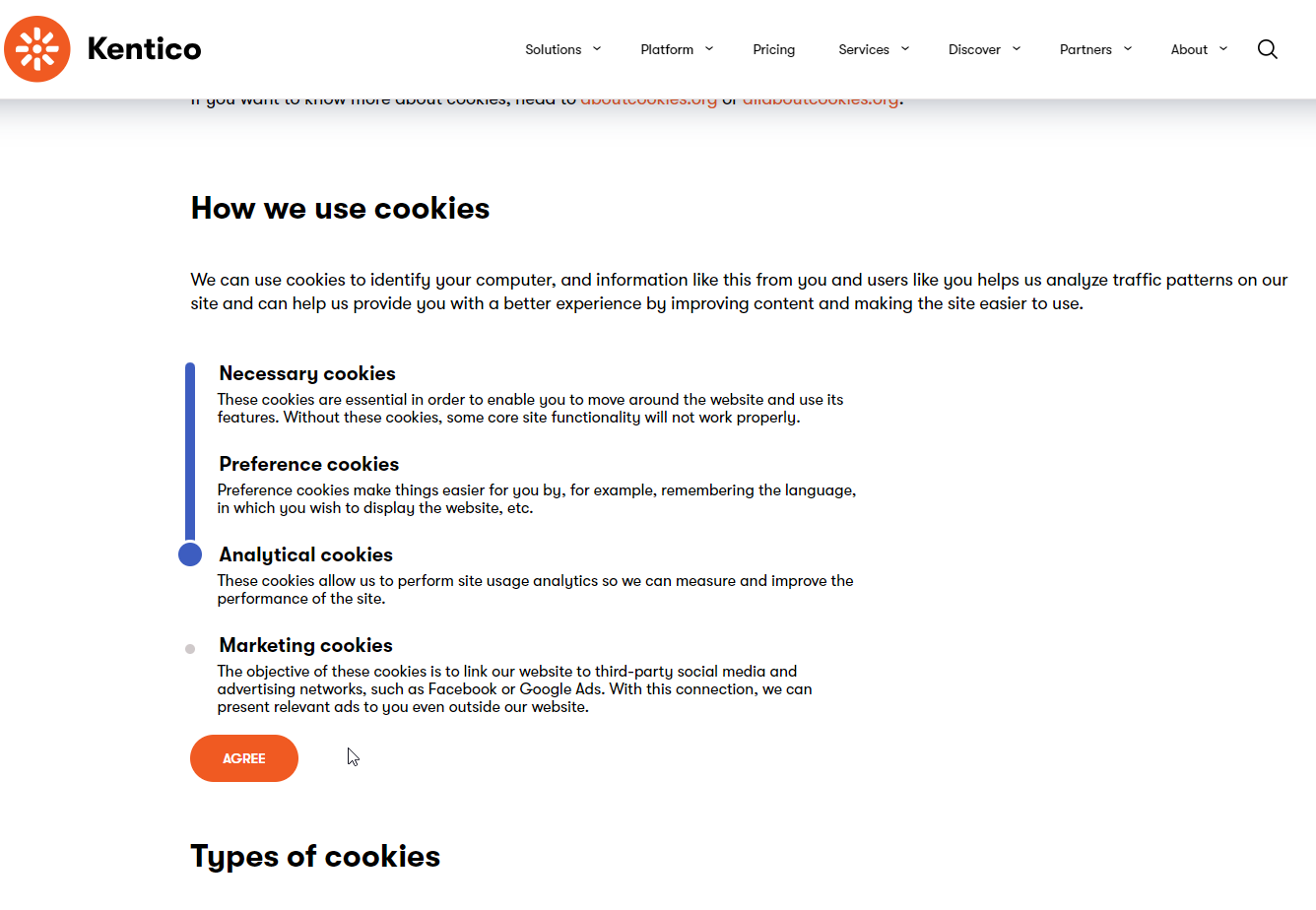
We will demonstrate how to create more granular cookie tiers than the built-in cookie levels using a widget, helper classes, and a custom controller to tie in with specially-designated consents.
Define the widget properties and view model
- Create the following folder structure in TrainingGuides.Web project: Features/DataProtection/Widgets/CookiePreferences.
- Create a
CookiePreferencesWidgetPropertiesclass that inherits fromIWidgetProperties, as outlined in the widget documentation. - Add properties to hold the header and description for the essential cookie level and the text for the submit button, and assign appropriate form components to each.
using Kentico.PageBuilder.Web.Mvc;
using Kentico.Xperience.Admin.Base.FormAnnotations;
namespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Widgets.CookiePreferences;
public class CookiePreferencesWidgetProperties : IWidgetProperties
{
/// <summary>
/// Essential cookie header.
/// </summary>
[TextInputComponent(
Label = "Essential cookie header",
Order = 10)]
public string EssentialHeader { get; set; } = string.Empty;
/// <summary>
/// Essential cookie description.
/// </summary>
[TextInputComponent(
Label = "Essential cookie description",
Order = 20)]
public string EssentialDescription { get; set; } = string.Empty;
/// <summary>
/// Button text.
/// </summary>
[TextInputComponent(
Label = "Button text",
Order = 30)]
public string ButtonText { get; set; } = string.Empty;
}
The Essential cookie level is not associated with a consent here, as the example site is designed such that essential cookies cannot be disabled. The other cookie levels, Preference, Analytical, and Marketing, also have headers and descriptions, but their data will not come from the widget properties. Instead, this data will be retrieved based on the consents mapped to each cookie level via the UI page set up earlier in this series:
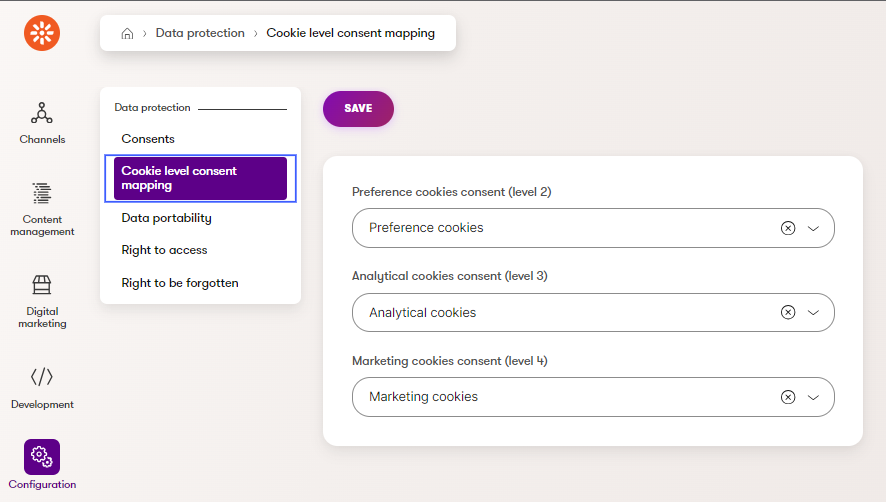
Next, create a view model for the widget in the CookiePreferences folder:
- Add properties corresponding to those from the widget properties.
EssentialHeaderEssentialDescriptionButtonText
- Include properties corresponding to the header and description of the Preference, Analytical, and Marketing cookie level consents.
- Define a property that holds the visitor’s existing selected cookie level so that the slider can be set to the correct position when the widget loads.
- Add a property to hold a snapshot of the cookie-level consent mapping. This will help to ensure that agreements are not created for the wrong consents if the mapping in the back-end changes after the widget is rendered for a site visitor but before their selection is submitted.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Html;
namespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Widgets.CookiePreferences;
public class CookiePreferencesWidgetViewModel
{
public string EssentialHeader { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public string EssentialDescription { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public string PreferenceHeader { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public HtmlString PreferenceDescriptionHtml { get; set; } = HtmlString.Empty;
public string AnalyticalHeader { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public HtmlString AnalyticalDescriptionHtml { get; set; } = HtmlString.Empty;
public string MarketingHeader { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public HtmlString MarketingDescriptionHtml { get; set; } = HtmlString.Empty;
public string ButtonText { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public int CookieLevelSelected { get; set; }
public string ConsentMapping { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public string BaseUrl { get; set; } = string.Empty;
}
Add an encryption service
To prevent a malicious visitor from tampering with their consent level, the mapping can be converted to a string, and then encrypted via a service that encrypts and decrypts strings.
Under the TrainingGuides.Web project, create a Features/DataProtection/Services folder.
Implement an interface for a string encryption service with two string methods, one for encrypting and one for decrypting. The interface will allow for flexibility in testing and alternative implementations.
C#IStringEncryptionService.csnamespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Services; public interface IStringEncryptionService { string EncryptString(string plainText); string DecryptString(string cipherText); }Implement this interface using .NET’s
Aesclass.C#AesEncryptionService.csusing System.Security.Cryptography; namespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Services; public class AesEncryptionService : IStringEncryptionService { private readonly string key; private readonly string iv; public AesEncryptionService(IConfiguration configuration) { key = configuration["AesEncryptionKey"] ?? string.Empty; iv = configuration["AesEncryptionIv"] ?? string.Empty; } /// <summary> /// Encrypts the provided string using Aes /// </summary> /// <param name="plainText">The string to be encrypted</param> /// <returns>An encrypted string</returns> /// <remarks>Relies on AesEncryptionKey and AesEncryptionIV in appsettings.json</remarks> /// <exception cref="ArgumentException">Thrown when AesEncryptionKey or AesEncryptionIV are not set in appsettings.json</exception> public string EncryptString(string plainText) { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(key) || string.IsNullOrEmpty(iv)) throw new ArgumentException("AesEncryptionKey and AesEncryptionIV must be set in appsettings.json"); if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(plainText)) return plainText; byte[] encrypted; // Create an Aes object // with the specified key and IV. using (var aesAlg = Aes.Create()) { aesAlg.Key = Convert.FromBase64String(key); aesAlg.IV = Convert.FromBase64String(iv); // Create an encryptor to perform the stream transform. var encryptor = aesAlg.CreateEncryptor(aesAlg.Key, aesAlg.IV); // Create the streams used for encryption. using var msEncrypt = new MemoryStream(); using var csEncrypt = new CryptoStream(msEncrypt, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write); using (var swEncrypt = new StreamWriter(csEncrypt)) { //Write all data to the stream. swEncrypt.Write(plainText); } encrypted = msEncrypt.ToArray(); } // Return the encrypted bytes from the memory stream. return Convert.ToBase64String(encrypted); } /// <summary> /// Decrypts the provided string using Aes /// </summary> /// <param name="cipherText">The string to be decrypted</param> /// <returns>A decrypted string</returns> /// <remarks>Relies on AesEncryptionKey and AesEncryptionIV in appsettings.json</remarks> public string DecryptString(string cipherText) { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(cipherText)) return cipherText; // Declare the string used to hold // the decrypted text. string plaintext = string.Empty; // Create an Aes object // with the specified key and IV. using (var aesAlg = Aes.Create()) { aesAlg.Key = Convert.FromBase64String(key); aesAlg.IV = Convert.FromBase64String(iv); // Create a decryptor to perform the stream transform. var decryptor = aesAlg.CreateDecryptor(aesAlg.Key, aesAlg.IV); // Create the streams used for decryption. using var msDecrypt = new MemoryStream(Convert.FromBase64String(cipherText)); using var csDecrypt = new CryptoStream(msDecrypt, decryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Read); using var srDecrypt = new StreamReader(csDecrypt); // Read the decrypted bytes from the decrypting stream // and place them in a string. plaintext = srDecrypt.ReadToEnd(); } return plaintext; } }
Key and IV
The Aes class uses a Key and IV during the encryption process. Keys are used by the encryption algorithm to map the encrypted ciphertext to its plaintext, and IVs or Initialization Vectors are used to essentially scramble the data and make patterns more difficult to recognize in the ciphertext.
These values can be generated dynamically, but the same values are necessary for both encryption and decryption, so for the purposes of this example, they must be stored somewhere accessible to both the widget, and the controller that handles the data submitted by the widget.
Store them as keys in the appsettings.json file.
{
...
"AesEncryptionKey": "a2VudGljbyBrZW50aWNvIGtlbnRpY28ga2VudGljbyA=",
"AesEncryptionIv": "a2VudGljbyBrZW50aWNvIA=="
}
You should use your own base64 strings for your Key and IV values. MAke sure they represent the same number of bytes as the examples.
The AesEncryptionService needs to be registered with the dependency injection container in order to be dynamically injected or resolved.
Create a singleton using this implementation for the service interface in the AddTrainingGuidesServices method in TrainingGuides.Web/ServiceCollectionExtensions.cs.
...
services.AddSingleton<IStringEncryptionService, AesEncryptionService>();
...
This extension method is already called in Program.cs on startup. It’s possible to register services directly in Program.cs, but it is best to create extension methods that group similar services for the sake of organization.
Create supplementary utilities
Some functionality will need to be used in multiple places. For instance, in this series, you will create a widget for users to configure their cookie level, as well as a banner to accept all cookies. There will be overlapping tasks that both of these components need to do, like retrieving the current cookie consent mapping, changing the TrainingGuides cookie level, and synchronizing this with the corresponding Xperience cookie level.
You need some shared code that can be used across all the cookie-related features.
In TrainingGuides.Web/Features/DataProtection/Services create an
ICookieConsentService. It will hold methods useful across multiple cookie-related features.Create a
CookieConsentServiceclass that implements theICookieConsentServiceinterface.In the interface, define a method signature for retrieving the cookie-level consent mapping asynchronously. Then, implement the method in the
CookieConsentServiceclass:C#CookieConsentService.csusing CMS.DataEngine; using TrainingGuides.DataProtectionCustomizations; namespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Services; /// <summary> /// Provides functionality for retrieving consents for contact. /// </summary> public class CookieConsentService : ICookieConsentService { private readonly IInfoProvider<CookieLevelConsentMappingInfo> cookieLevelConsentMappingInfoProvider; public CookieConsentService(IInfoProvider<CookieLevelConsentMappingInfo> cookieLevelConsentMappingInfoProvider) { this.cookieLevelConsentMappingInfoProvider = cookieLevelConsentMappingInfoProvider; } /// <summary> /// Gets the current cookie level consent mapping if it exists. /// </summary> /// <returns>A <see cref="CookieLevelConsentMappingInfo"/> object representing the project's current mappings, <see cref="null"/> if no mapping exists.</returns> public async Task<CookieLevelConsentMappingInfo?> GetCurrentMapping() { var currentMapping = await cookieLevelConsentMappingInfoProvider.Get().GetEnumerableTypedResultAsync(); return currentMapping.FirstOrDefault(); } }To be continued …
You will expand the
CookieConsentServiceclass and interface with additional functionality throughout this series.Just like with the
AesEncryptionServiceabove, remember to register yourCookieConsentServicewith the dependency injection container in TrainingGuides.Web/ServiceCollectionExtensions.cs:C#ServiceCollectionExtensions.cs... services.AddSingleton<ICookieConsentService, CookieConsentService>(); ...Create a Shared folder under TrainingGuides.Web/Features/DataProtection and add an enumeration to represent the cookie consent levels the widget will use.
Although the enumeration is currently used only by the cookie preferences widget, we recommend adding it to a Shared folder, as other components will rely on it later in this series.
C#CookieConsentLevel.csnamespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Shared; /// <summary> /// Cookie consent level types. /// </summary> public enum CookieConsentLevel { /// <summary> /// Cookie consent level is not set. /// </summary> NotSet = 0, /// <summary> /// Only essential cookies which are necessary for running the system. /// </summary> Essential = 1, /// <summary> /// Cookies for user preferences. /// </summary> Preference = 2, /// <summary> /// Cookies for site usage analysis. /// </summary> Analytical = 3, /// <summary> /// All cookies enabling to collect information about visitor. /// </summary> Marketing = 4 }In the same Shared folder, define a class called
CookieNames, which will hold constants with the names of cookies we want to register and reference throughout the project:COOKIE_ACCEPTANCEindicates whether the visitor has agreed to any cookie levelCOOKIE_CONSENT_LEVELrepresents the level of consent the visitor has agreed toC#CookieNames.csnamespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Shared; /// <summary> /// Contains names of all custom cookies extending the solution. Each need to be registered in <see cref="CookieRegistrationModule"/>. /// </summary> public static class CookieNames { // System cookies public const string COOKIE_CONSENT_LEVEL = "trainingguides.cookieconsentlevel"; public const string COOKIE_ACCEPTANCE = "trainingguides.cookielevelselection"; }As the comment indicates, these cookies correspond to the System cookie level in Xperience. This is not to be confused with the more granular cookie levels in the widget, which are specific to this project. Synchronizing these two cookie levels will be covered in a later section.
Now, you can register these cookie names when the app starts so that they can easily be added, updated, and removed from the visitor’s browser:
Navigate to the Program.cs file in the TrainingGuides.Web project.
In the area where you configure the application builder, add cookies using the
Systemlevel to theCookieLevelOptions.CookieConfigurationsdictionary.Whenever you use the default
ICookieAccessorimplementation to set a cookie in a visitor’s browser, Xperience compares the cookie level defined here to that visitor’s current cookie level in order to decide whether or not the cookie is allowed.C#Program.cs... builder.Services.Configure<CookieLevelOptions>(options => { options.CookieConfigurations.Add(CookieNames.COOKIE_CONSENT_LEVEL, CookieLevel.System); options.CookieConfigurations.Add(CookieNames.COOKIE_ACCEPTANCE, CookieLevel.System); }); ...If you want to use Xperience to manage any custom cookies with the cookie helper, e.g., from 3rd party systems, register them similarly, choosing an appropriate built-in cookie level.
Add the view component
With the reusable code in place, you can return to the widget. As mentioned in the widget documentation, widgets that need complex business logic should be based on view components.
- Add a file to the CookiePreferences widget folder called
CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent.cs. - Register the class as a widget, referencing
CookiePreferencesWidgetProperties. - Define a method called
InvokeAsync, which retrieves all consents that are currently mapped to cookie levels from the database and uses them to populate the corresponding view model fields. - Turn the mapping into a dictionary and convert it to a JSON string to be encrypted in the
ConsentMappingview model property.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Html;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ViewComponents;
using CMS.DataProtection;
using CMS.DataEngine;
using Kentico.Content.Web.Mvc.Routing;
using Kentico.PageBuilder.Web.Mvc;
using Kentico.Web.Mvc;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using TrainingGuides.DataProtectionCustomizations;
using TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Services;
using TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Shared;
using TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Widgets.CookiePreferences;
using TrainingGuides.Web.Features.Shared.Services;
[assembly: RegisterWidget(
identifier: CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent.IDENTIFIER,
viewComponentType: typeof(CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent),
name: "Cookie preferences",
propertiesType: typeof(CookiePreferencesWidgetProperties),
Description = "Displays a cookie preferences.",
IconClass = "icon-cookie")]
namespace TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Widgets.CookiePreferences;
public class CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent : ViewComponent
{
private const string CONSENT_MISSING_HEADER = "CONSENT NOT FOUND";
private readonly HtmlString consentMissingDescriptionHtml = new("Please ensure that a valid consent is mapped to this cookie level in the Data protection application.");
/// <summary>
/// Widget identifier.
/// </summary>
public const string IDENTIFIER = "TrainingGuides.CookiePreferencesWidget";
private readonly IInfoProvider<ConsentInfo> consentInfoProvider;
private readonly IStringEncryptionService stringEncryptionService;
private readonly IPreferredLanguageRetriever preferredLanguageRetriever;
private readonly ICookieConsentService cookieConsentService;
private readonly ICookieAccessor cookieAccessor;
private readonly IHttpRequestService httpRequestService;
/// <summary>
/// Creates an instance of <see cref="CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent"/> class.
/// </summary>
public CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent(
IInfoProvider<ConsentInfo> consentInfoProvider,
IStringEncryptionService stringEncryptionService,
IPreferredLanguageRetriever preferredLanguageRetriever,
ICookieConsentService cookieConsentService,
ICookieAccessor cookieAccessor,
IHttpRequestService httpRequestService)
{
this.consentInfoProvider = consentInfoProvider;
this.stringEncryptionService = stringEncryptionService;
this.preferredLanguageRetriever = preferredLanguageRetriever;
this.cookieConsentService = cookieConsentService;
this.cookieAccessor = cookieAccessor;
this.httpRequestService = httpRequestService;
}
/// <summary>
/// Invokes the widget view component
/// </summary>
/// <param name="properties">The properties of the widget</param>
/// <returns>The view for the widget</returns>
public async Task<ViewViewComponentResult> InvokeAsync(CookiePreferencesWidgetProperties properties)
{
var currentMapping = await cookieConsentService.GetCurrentMapping();
// Get consents
var preferenceCookiesConsent = await consentInfoProvider.GetAsync(currentMapping?.PreferenceConsentCodeName.FirstOrDefault());
var analyticalCookiesConsent = await consentInfoProvider.GetAsync(currentMapping?.AnalyticalConsentCodeName.FirstOrDefault());
var marketingCookiesConsent = await consentInfoProvider.GetAsync(currentMapping?.MarketingConsentCodeName.FirstOrDefault());
string mapping = GetMappingString(currentMapping);
return View("~/Features/DataProtection/Widgets/CookiePreferences/CookiePreferencesWidget.cshtml", new CookiePreferencesWidgetViewModel
{
EssentialHeader = properties.EssentialHeader,
EssentialDescription = properties.EssentialDescription,
PreferenceHeader = preferenceCookiesConsent.ConsentDisplayName ?? CONSENT_MISSING_HEADER,
PreferenceDescriptionHtml = new HtmlString((await preferenceCookiesConsent.GetConsentTextAsync(preferredLanguageRetriever.Get())).FullText) ?? consentMissingDescriptionHtml,
AnalyticalHeader = analyticalCookiesConsent.ConsentDisplayName ?? CONSENT_MISSING_HEADER,
AnalyticalDescriptionHtml = new HtmlString((await analyticalCookiesConsent.GetConsentTextAsync(preferredLanguageRetriever.Get())).FullText) ?? consentMissingDescriptionHtml,
MarketingHeader = marketingCookiesConsent.ConsentDisplayName ?? CONSENT_MISSING_HEADER,
MarketingDescriptionHtml = new HtmlString((await marketingCookiesConsent.GetConsentTextAsync(preferredLanguageRetriever.Get())).FullText) ?? consentMissingDescriptionHtml,
CookieLevelSelected = CMS.Helpers.ValidationHelper.GetInteger(cookieAccessor.Get(CookieNames.COOKIE_CONSENT_LEVEL), 1),
ConsentMapping = stringEncryptionService.EncryptString(mapping),
ButtonText = properties.ButtonText,
BaseUrl = httpRequestService.GetBaseUrl()
});
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets a serialized string representation of the cookie level consent mapping
/// </summary>
/// <param name="currentMapping">A CookieLevelConsentMappingInfo object</param>
/// <returns>A JSON serialized sting representation of the mapping</returns>
private string GetMappingString(CookieLevelConsentMappingInfo? currentMapping)
{
var mapping = currentMapping != null
? new Dictionary<int, string>
{
{ (int)CookieConsentLevel.Preference, currentMapping.PreferenceConsentCodeName.FirstOrDefault() ?? string.Empty },
{ (int)CookieConsentLevel.Analytical, currentMapping.AnalyticalConsentCodeName.FirstOrDefault() ?? string.Empty },
{ (int)CookieConsentLevel.Marketing, currentMapping.MarketingConsentCodeName.FirstOrDefault() ?? string.Empty }
}
: [];
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(mapping).ToString();
}
}
Make the widget identifier available
In the future, you may need to limit which widgets are available in different Page Builder sections and zones. To make this easier, add the identifier of the new Cookie preferences widget to the ComponentIdentifiers class.
- Navigate to TrainingGuides.Web/ComponentIdentifiers.cs.
- Add a new static class called
Widgetsinside theComponentIdentifiersclass if it does not already exist. - Add a string constant referencing the identifier of the widget, defined in the
CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent.
public static class ComponentIdentifiers
{
...
public static class Widgets
{
...
public const string COOKIE_PREFERENCES = CookiePreferencesWidgetViewComponent.IDENTIFIER;
...
}
...
}
Define the view
The widget will use AJAX, so install the ASPNetCore.Unobtrusive.Ajax NuGet package and add this line to
Program.cswhere the service collection is being assembled.C#Program.cs... builder.Services.AddUnobtrusiveAjax(); ...This allows the widget’s view to use the
Html.AjaxBeginFormextension.Create an AJAX form that posts to ~/cookies/submit. (We’ll add a controller action to handle this POST request later.)
Use a range input for the cookie slider, selecting a value between 1 and 4, and include the encrypted mapping in a hidden field.
Define an area to write a result message, and use an unordered list to display the titles and texts of the consents.
The CSS that allows the slider to align with the bullet points is beyond the scope of this example, but feel free to view it in the repository.
@using CMS.Helpers
@using TrainingGuides.Web.Features.Shared.Services
@using TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Shared
@using TrainingGuides.Web.Features.DataProtection.Widgets.CookiePreferences
@model CookiePreferencesWidgetViewModel;
@{
Layout = null;
var messageId = "cookiePreferencesMessage";
}
@using (Html.AjaxBeginForm("CookiePreferences", "Cookies", new AjaxOptions
{
HttpMethod = "POST",
InsertionMode = InsertionMode.Replace,
UpdateTargetId = messageId
}, new { action = $"{Model.BaseUrl}/cookies/submit" }))
{
<div class="container">
<div>
<input id="ConsentMapping" name="ConsentMapping" type="hidden" value="@Model.ConsentMapping" />
<div class="cookie-preferences__levels">
<div class="cookie-preferences__selector" id="js-cookie-preferences__selector">
<div class="cookie-preferences__range-fill" id="range-fill"></div>
<input id="CookieLevelSelected" name="CookieLevelSelected" type="range" min="1" max="4" step="1" class="cookie-preferences__range-slider" value="@Model.CookieLevelSelected" />
</div>
<ul class="cookie-preferences__options">
<li class="cookie-preferences__option" data-value="1">
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-header">@Model.EssentialHeader</span>
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-description">@Model.EssentialDescription</span>
</li>
<li class="cookie-preferences__option" data-value="2">
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-header">@Model.PreferenceHeader</span>
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-description">@Model.PreferenceDescriptionHtml</span>
</li>
<li class="cookie-preferences__option" data-value="3">
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-header">@Model.AnalyticalHeader</span>
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-description">@Model.AnalyticalDescriptionHtml</span>
</li>
<li class="cookie-preferences__option" data-value="4">
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-header">@Model.MarketingHeader</span>
<span class="cookie-preferences__option-description">@Model.MarketingDescriptionHtml</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<button class="btn tg-btn-secondary text-uppercase mt-4 cookie-preferences__button" type="submit" name="button">
@Model.ButtonText
</button>
<div id="@messageId" class="cookie-preferences__message"></div>
</div>
</div>
}